We are grateful for funding for our research from these agencies
Spectroscopy of Solution Species in Vacuo
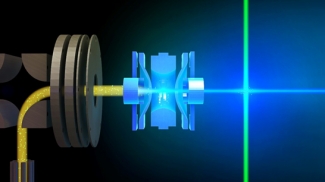
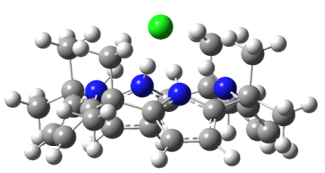
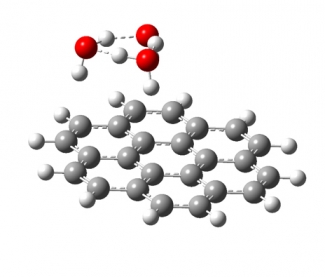
Much of the behavior of important molecular species is only known in a condensed phase environment (mostly solutions). Probing the details of molecular properties and molecular interactions in these often very complex environments can be difficult, as the interaction with the solvent changes the properties of the solute and broadens its spectroscopic response. All these effects tend to obscure important details of molecular properties from spectroscopic characterization. The presence of a chemical environment also presents a challenge for computational analysis, since the description of a molecule including its solvation shell(s) is often beyond the reach of high-level quantum chemistry methods, and the use of continuum models is an approximation that ignores important effects such as hydrogen bonding. In order to circumvent many of these problems, we study mass-selected molecular and cluster ions as isolated entities in vacuo.
Learn more about our experimental apparatus, and discover our current work on molecular recognition complexes, PAH-water clusters, and biomolecule detection.
High Pressure Response of Materials
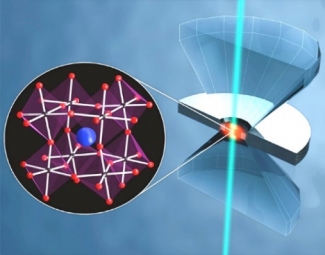
Very high pressures (up to tens of GPa) allow access to unconventional thermodynamic parameters, and open avenues to explore new chemical and physical properties of materials. Different from the influence of temperature, pH and chemical composition, which have multiple effects on a system (total energy, volume, covalent bonds), perturbation of molecules and materials by hydrostatic pressure only changes inter- and intramolecular distances. In addition, phase changes can be triggered by increased pressure, leading to materials with new optical and electronic properties.
Learn about our work on perovskites and other materials.