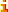4/22. Waterfall model of a Schwarzschild Black Hole
Gullstrand-Painlevé (1921) version of the Schwarzschild metric:
\(
d s^2
=
- \, d t_{\rm ff}^2
+ ( d r - v \, d t_{\rm ff} )^2
+
r^2 d o^2
\)
where
\(v = \sqrt{2 G M / r}\)
is the Newtonian escape velocity,
and
\(t_{\rm ff}\)
is the time attached to a free-fall observer.
Free-fall time is related to Schwarzschild time by
\(d t_{\rm ff} = d t - v \, d r / ( 1 - v^2 )\).
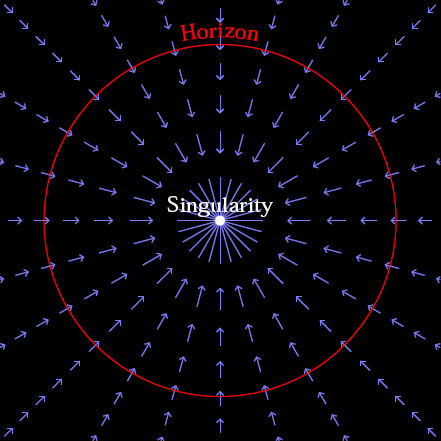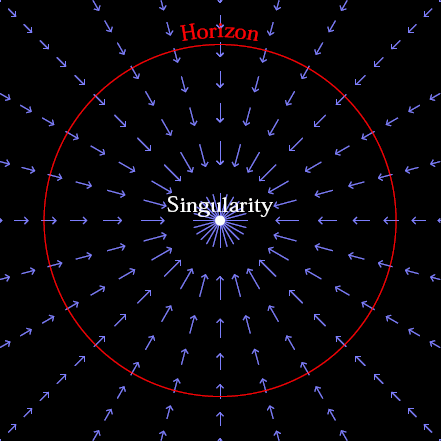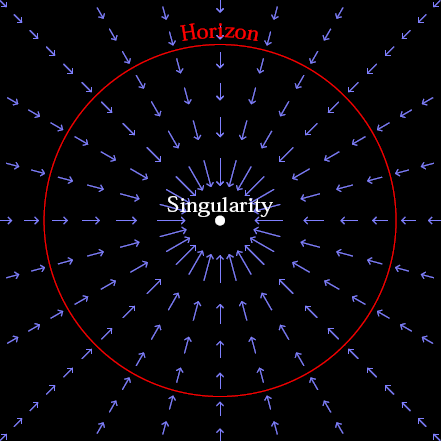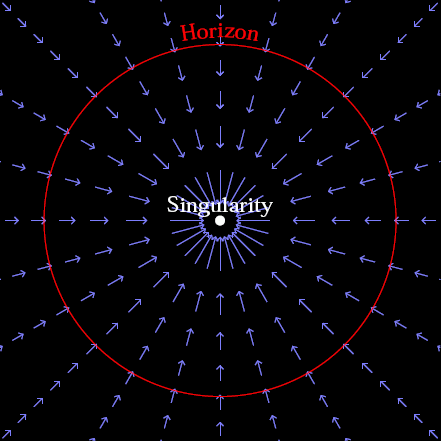
 5/22. Fishies
5/22. Fishies