A theme of this course has been the posing of thought-provoking questions
which we debate in class.
Sometimes it takes as much as half an hour to debate a single question.
Some questions are multiple choice, others open-ended.
The multiple choice questions do not all have unique answers:
sometimes several answers are right;
sometimes answers can be partially right and partially wrong.
Such ambiguity is the bane of exams,
but a boon in discussion.
| The Scale of the Universe |
|---|

|
What has the speed of air molecules in this room got to do with
how fast present day spacecraft go?
| |
|

|
About how fast are individual air molecules in this room moving?
(a) They hardly move;
(b) As fast as the wind;
(c) The speed of sound;
(d) The speed of light.
| |
|

|
About how fast is the speed of sound?
(a) People speed (1 m/s);
(b) Car speed (10 m/s);
(c) Jet speed (1 km/s);
(d) Light speed (300,000 km/s).
| |
|

|
What is the gravitational escape velocity from the Earth's surface?
(a) About the speed of sound (1 km/s);
(b) Several times the speed of sound (10 km/s);
(c) Light speed (300,000 km/s);
(d) Infinity (escape is impossible).
| |
|

|
It is possible to escape the Earth's gravity because:
(a) There is no gravity in space;
(b) Earth's gravity extends to infinity, but it gets weaker as you go farther away.
| |
|

|
About how fast does a spacecraft go? Why?
|

|
What difficulties are involved in traveling to the stars?
|

|
How do astronomers measure distances to stars:
(a) Spacecraft equipped with long tape measures;
(b) Laser-ranging;
(c) Trigonometric parallax;
(d) ``Standard candles'',
plus the inverse square law of brightness with distance.
|
|

|
What is the purpose of the Foucault Pendulum (1851)
hanging in the Gamow Tower?
(a) To tell time;
(b) To demonstrate Newton's laws of motion;
(c) To demonstrate that
|
Period
=
|
æ
ç
è |
g
length
|
ö
÷
ø |
1/2
|
; |
|
(d) To demonstrate that the Earth rotates.
|
|

|
This is a part of the
Hubble Deep Field.
The image is so deep that it goes pretty much all the way to the horizon,
the edge of the observable Universe
(the horizon is determined by how far light can travel
during the age of the Universe).
To a certain level,
we are seeing all the galaxies there are as far as the horizon.
Virtually everything in the image,
not only the big bright things,
but also all the little faint blobs of light,
are galaxies.
Estimate roughly how many galaxies there are in the picture.

The field shown is 150 arcseconds by 38 arcseconds in angular size.
Estimate the number of galaxies in the presently observable Universe.
|
|
| Light |
|---|

|
Compare the light from
a high wattage tungsten filament bulb
to that from a mercury vapor lamp.
Which white is whiter?
|

|
A filter that absorbs yellow light,
when inserted into the path of a spectrum of white light passed through
through a prism, will:
(a) produce a dark band of absorption of yellow light;
(b) will absorb not only yellow, but also the yellow part of green,
making the green part of the spectrum look blue.
|

|
How does fluorescent dye work?
The atoms of fluorescent dye:
(a) have an electromagnetic aura;
(b) are hotter than their surroundings;
(c) are extra efficient at absorbing and emitting light;
(d) convert ultraviolet to visible light;
(e) convert infrared to visible light.
|

|
The frequencies at which an atom absorbs light:
(a) depend on what type of atom (element) it is;
(b) correspond to the absolute energy levels of the atom;
(c) correspond to differences in energy levels of the atom;
(d) are the same as the frequencies at which the atom emits;
(e) are exacly the oppositve of the frequencies at which the atom emits.
|

|
In light waves, what is it that wiggles?
|
|
| The Sun |
|---|

|
How did Eddington estimate the temperature at the center of the Sun?
Hint:
The Sun's gravitational escape velocity is 618 km/s.
|

|
You are orbiting the Earth in a space shuttle, hard on the heels
of another space shuttle.
To overtake the space shuttle ahead, do you:
(a) speed up;
(b) slow down?
|

|
If a gravitating system loses energy, it:
(a) cools down (temperature decreases);
(b) heats up (temperature increases)?
|

|
Why doesn't the Sun explode like a nuclear bomb?
|

|
How can the corona at ~ 106 K be hotter than
the chromosphere at ~ 5,000 K?
|
|
| Stars |
|---|

|
When should
Ha,
Hb,
Hg,
...,
absorption in a star be strong?
(a) When the n = 1 (ground) level is most populated;
(b) When the n = 2 level is most populated;
(c) When the n = 3, 4, 5, ..., levels are most populated;
(d) When H is mostly ionized?
|

|
When is the n = 2 level of H most populated?
(a) low Temperature;
(b) intermediate Temperature;
(c) high Temperature?
|

|
If
Ha
is weak in stars both colder and hotter than A stars,
how can you tell the temperature?
(a) Wien's law;
(b) the Stefan-Boltzmann law;
(c) the strengths of spectral lines of other elements or ions.
|

|
The stars in a star cluster all have the same:
(a) distance;
(b) temperature;
(c) luminosity;
(d) age;
(e) composition;
(f) radius;
(g) composition.
|

|
How much brighter (apparently) is the Sun than Sirius?
|

|
If you put the Pleiades 2 times further away, they would appear:
(a) the same apparent brightness;
(b) 2 times fainter;
(c) 4 times fainter;
(d) 8 times fainter;
(e) 16 times fainter.
|

|
The Main Sequence is a sequence of stars of different:
(a) distance;
(b) temperature;
(c) luminosity;
(d) age;
(e) composition;
(f) radius;
(g) mass.
|

|
The Hertzsprung-Russell diagrams of different clusters look different
because they have different:
(a) distance;
(b) composition;
(c) age;
(d) range of stellar masses?
|

|
What happens to a star when it runs out of H at its core?
(a) The core cools down (core Temperature goes down);
(b) The core contracts and heats up (core Temperature goes up);
(c) The star evolves along the Main Sequence;
(d) The star becomes a Red Giant;
(e) The star becomes a White Dwarf;
(f) The star destroys all life on Earth.
|

|
Eddington's Paradox:
If a star, when it runs out of fuel, heats up, how can it ever cool down?
(a) It never cools;
(b) It cools, held up by electron degeneracy pressure
(the pressure from the quantum-mechanical zero-point motion of electrons);
(c) It cools, held up by nuclear degeneracy pressure
(the pressure from the quantum-mechanical zero-point motion of nuclei);
(d) It cools, held up by the `strong' nuclear force;
(e) It eventually collapses to a black hole.
|

|
Why is the surface temperature of stars always of order 104 K?
It's the temperature where:
(a) thermal velocity = gravitational escape velocity;
(b) H gets ionized;
(c) H fuses into He;
(d) electrons are degenerate.
|
|
| Relativity and Black Holes |
|---|

|
From Einstein's assertion
that the speed of light is the same for all observers,
it follows that,
if light is emitted from a point where an observer is,
then the observer will always find self at the center of the
expanding sphere of light, irrespective of the observer's motion.
(a) True;
(b) False?
|

|
Are these boxes the same?
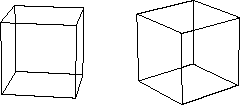
In relativity, how long an interval of space or time appears
depends on your perspective.
Observers moving relative to each other have different perspectives.
|

|
If nothing can get out of a black hole,
how come its gravity can get out?
|

|
If the Earth were compressed to a black hole,
how big would it be?
[Hint:
1 Mearth » 3 × 10-6 Msun.
The Schwarzschild radius of a black hole of 1 Msun
is about 3 km.]
|

|
How big/massive/hot are evaporating black holes?
How long does an evaporating black hole last?
What would an evaporating black hole look like?
When an evaporating black hole explodes, how big is the explosion?
|

|
What happens to the singularity when a black hole evaporates?
|

|
What is the Hawking temperature of the Earth?
|

|
If you went near a mini black hole, what would it feel like?
Would you feel its gravity? Would you be torn apart?
What if you tried to hold it?
Would it hurt?
|

|
What would happen if a black hole were made in a particle accelerator?
Is that likely to happen?
|

|
Suppose a mini black hole were dropped into the Earth.
What would happen?
Would the black hole eat the Earth?
|
|